
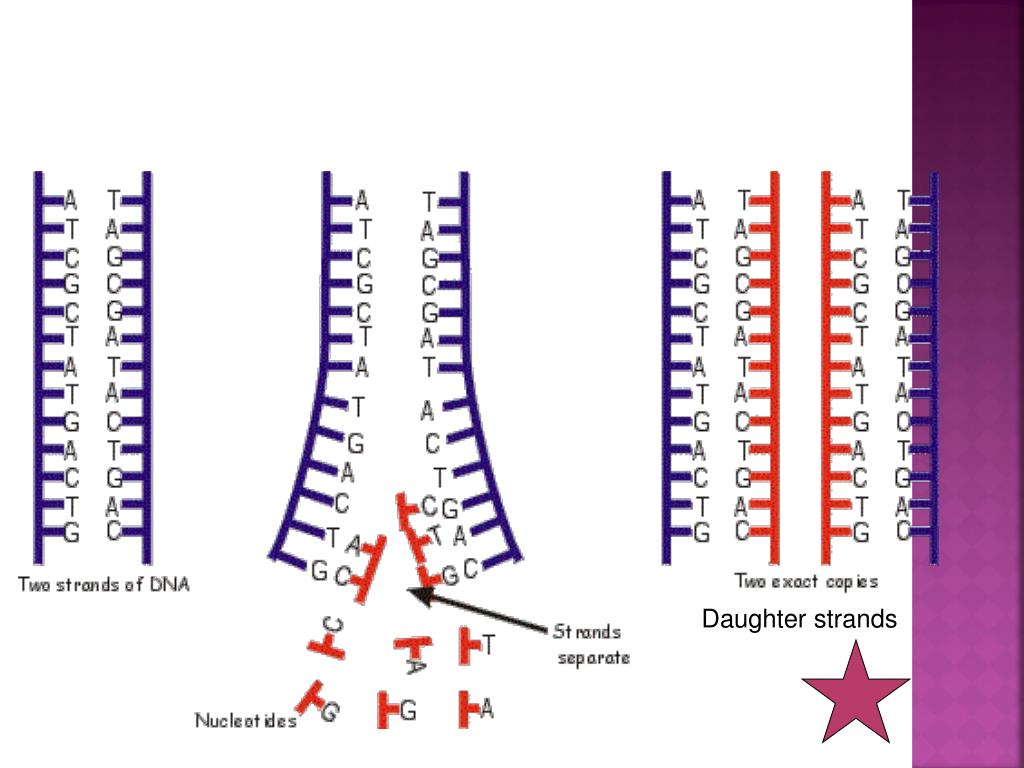
DNA and RNA bases are also held together by chemical bonds and have specific base pairing rules. However, the “bases” of RNA differ from those of DNA in that thymine (T) is replaced by uracil (U) in RNA. RNA is a molecule that is chemically similar to DNA, and also contains repeating nucleotide subunits. Bases that bond together are known as complementary.ĭuring transcription, DNA is converted to messenger RNA (mRNA) by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. Adenine and thymine form base pairs that are held together by two bonds, while cytosine and guanine form base pairs that are held together by three bonds. Additionally, there are base pairing rules that determine which bases can bond with each other. This bonding holds the two chains together. A base on one of the chains that makes up DNA is chemically bonded to a base on the other chain. There are four different types of nucleotides in DNA, and they differ from one another by the type of base that is present: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Each chain is made up of repeating subunits called nucleotides that are held together by chemical bonds. The chains twist to form a double helix in shape.

A molecule of DNA consists of two chains that are wrapped around each other. Image courtesy of the Human Genome Research InstituteĭNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, and it is the carrier of genetic information within a cell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
